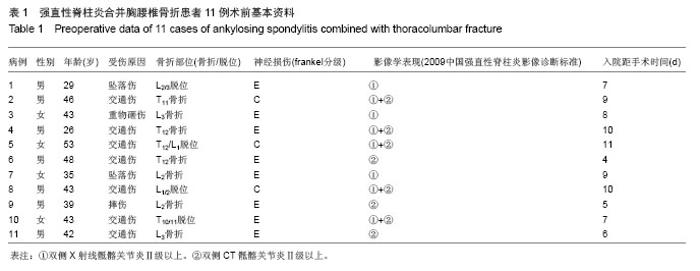
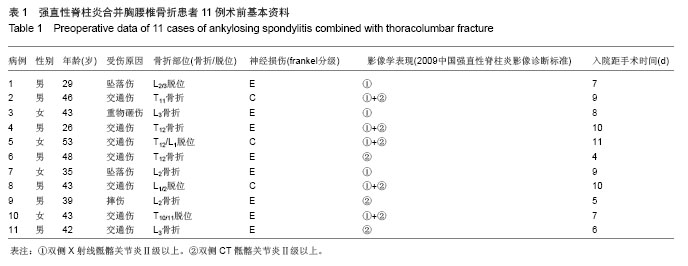
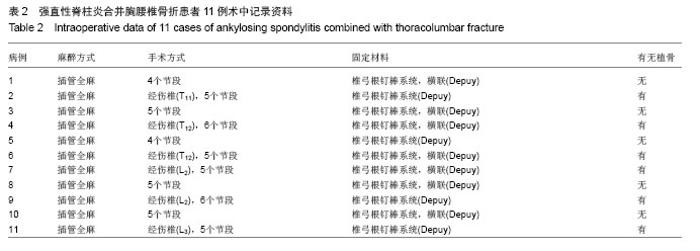
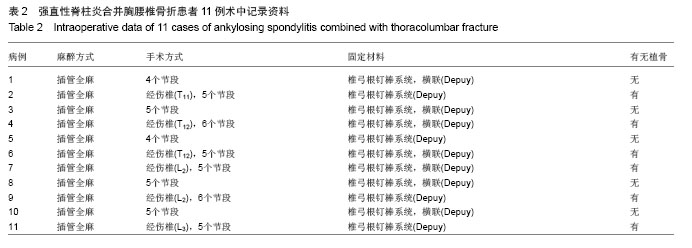
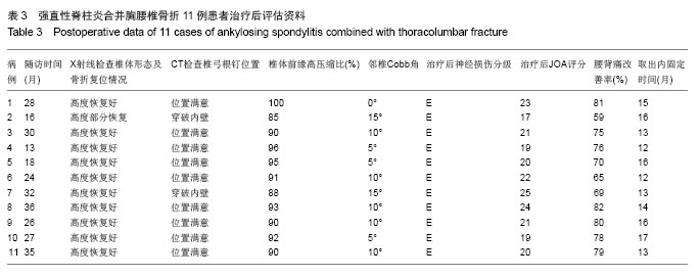
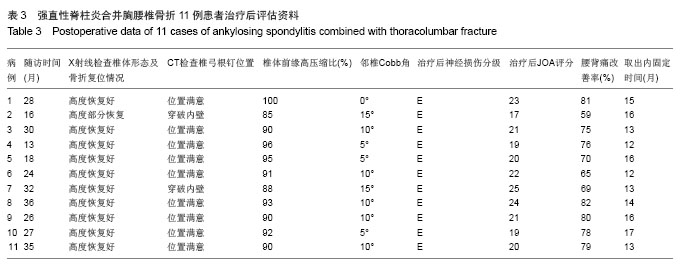
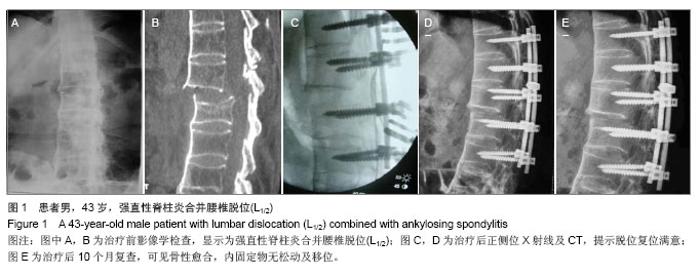
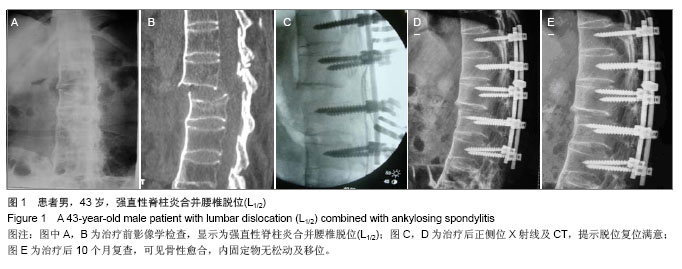
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (9): 1368-1373.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.09.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Multi-segment transpedicle spinal fixation for thoracolumbar fractures with ankylosing spondylitis: one-year follow-up
Wu Xing-guo, Huang Jian, Jiang Yu-qing, Guo Wei-kang, Wang Jun
- the Fourth Department of Orthopedics, Meizhou Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Meizhou 514031, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2014-02-26Published:2014-02-26 -
About author:Wu Xing-guo, Master, Associate chief physician, the Fourth Department of Orthopedics, Meizhou Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Meizhou 514031, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Xing-guo, Huang Jian, Jiang Yu-qing, Guo Wei-kang, Wang Jun. Multi-segment transpedicle spinal fixation for thoracolumbar fractures with ankylosing spondylitis: one-year follow-up[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(9): 1368-1373.
share this article
| [1]Wanders A, Landewé R, Dougados M, et al.Association between radiographic damage of the spine and spinal mobility for individual patients with ankylosing spondylitis: can assessment of spinal mobility be a proxy for radiographic evaluation?Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(7):988-994.[2]刘海春,陈允震,张剑锋,等.强直性脊柱炎颈椎骨折诊断及后路内固定治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2004,12(18):1369-1372.[3]Foo D, Sarkarati M, Marcelino V.Cervical spinal cord injury complicating ankylosing spondylitis.Paraplegia. 1985;23(6): 358-363.[4]Trent G, Armstrong GW, O'Neil J.Thoracolumbar fractures in ankylosing spondylitis. High-risk injuries.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;227:61-66.[5]Hunter T, Dubo HI.Spinal fractures complicating ankylosing spondylitis. A long-term followup study.Arthritis Rheum. 1983; 26(6):751-759.[6]Wang YF, Teng MM, Chang CY,et al. Imaging manifestations of spinal fractures in ankylosing spondylitis.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26(8):2067-2076.[7]Chang KW, Tu MY, Huang HH,et al.Posterior correction and fixation without anterior fusion for pseudoarthrosis with kyphotic deformity in ankylosing spondylitis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(13):E408-413.[8]李前龙,王华军,李义凯,等.强直性脊柱炎引起的骨质疏松性椎体骨折风险评估[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2009,15(11):864-867.[9]魏萌,谢庆云,杨晓平,等.强直性脊柱炎患者股骨密度与腰椎椎体骨折的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(28): 5575-5579.[10]Cornefjord M, Alemany M, Olerud C.Posterior fixation of subaxial cervical spine fractures in patients with ankylosing spondylitis.Eur Spine J. 2005;14(4):401-408.[11]高梁斌,李佛保,李健,等.全髋置换和多节段截骨治疗强直性脊柱炎驼背并髋骨性屈曲强直[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版,2005, 26(5):559-562.[12]Boachie-Adjei O, Ferguson JA, Pigeon RG,et al. Transpedicular lumbar wedge resection osteotomy for fixed sagittal imbalance: surgical technique and early results.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(4):485-492.[13]Kawahara N, Tomita K, Baba H,et al. Closing-opening wedge osteotomy to correct angular kyphotic deformity by a single posterior approach.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(4): 391-402.[14]Pigge RR, Scheerder FJ, Smit TH,et al.Effectiveness of preoperative planning in the restoration of balance and view in ankylosing spondylitis.Neurosurg Focus. 2008; 24(1):E7. [15]陈伟,刘玉珂,张斌青,等.强直性脊柱炎脊柱骨折的影像学表现及损伤特点[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2013,11(1):101-104.[16]尹韶晗,陈东,姜涛,等.强直性脊柱炎并发颈胸椎骨折的影像学分析[J].武警后勤学院学报:医学版,2012,21(12):974-977.[17]郑建军.强直性脊柱炎胸椎应力性骨折的影像学诊断[J].河北医科大学学报,2012,33(6):733-734.[18]陈建宇,杨泽宏,刘庆余,等.强直性脊柱炎脊柱骨折的影像学表现[J].中国医学影像技术,2010,26(8):1534-1537.[19]曾忠友,金才益,江春宇,等.强直性脊柱炎胸腰椎骨折的损伤特点和治疗[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(2):135-138.[20]钱邦平,邱勇,王斌,等.强直性脊柱炎患者胸腰椎应力骨折的临床及影像学特点[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2008,18(10):747- 751.[21]Heining CF,Boyd BM. One stage vertebrectomy or eggshell procedure. Orthop Trans.1985;9:130-136.[22]Murrey DB, Brigham CD, Kiebzak GM,et al.Transpedicular decompression and pedicle subtraction osteotomy (eggshell procedure): a retrospective review of 59 patients.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(21):2338-2345. [23]Suk SI, Kim JH, Kim WJ,et al.Posterior vertebral column resection for severe spinal deformities.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(21):2374-2382.[24]Lenke LG, O'Leary PT, Bridwell KH,et al.Posterior vertebral column resection for severe pediatric deformity: minimum two-year follow-up of thirty-five consecutive patients.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(20):2213-2221. [25]Berven SH, Deviren V, Smith JA, et al. Management of fixed sagittal plane deformity: results of the transpedicular wedge resection osteotomy.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(18): 2036-2043.[26]Bridwell KH.Decision making regarding Smith-Petersen vs. pedicle subtraction osteotomy vs. vertebral column resection for spinal deformity.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(19 Suppl): S171-178.[27]张文生,郑闽前,邹国友,等.强直性脊柱炎胸腰椎骨折手术方法的选择[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(9):778-781.[28]黄玉国,李永民,申勇.强直性脊柱炎脊柱骨折的临床特点和手术治疗策略[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(7):644-646.[29]杜辉,付勤,陈洪亮,等.强直性脊柱炎合并胸腰椎骨折的外科治疗[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(5):448-449.[30]史相钦,王少纯,赵刚,等.椎弓根固定治疗强直性脊柱炎合并胸腰椎骨折[J].光明中医,2011,26(9):1820-1821.[31]王瑞,孔晓川,李健,等.椎弓根固定治疗强直性脊柱炎合并胸腰椎骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(4):381-383.[32]李贵山,方永刚,罗建军,等.强直性脊柱炎合并胸腰椎骨折的手术冶疗[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂, 2010,25(9):809-810.[33]李宝俊,丁文元,申勇,等.强直性脊柱炎伴胸腰椎骨折的手术治疗[J].首都医科大学学报,2008,29(6):677-680.[34]Escosa Bagé M, García Navarrete E, Pascual Garvi JM,et al.Surgical treatment of spondylodiscitis in ankylosing spondylitis. Two cases report.Rev Neurol. 2001; 33(10): 964-966.[35]王岩,张永刚,郑国权,等.脊柱去松质骨截骨治疗僵硬性脊柱侧凸的有效性及安全性分析[J].中华外科杂志,2010,48(22): 1701-1704.[36]徐龙伟,季卫平,李浩,等.老年性骨质疏松性不稳定胸腰椎骨折的手术治疗[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(1):19-21.[37]Kiaer T, Gehrchen M.Transpedicular closed wedge osteotomy in ankylosing spondylitis: results of surgical treatment and prospective outcome analysis.Eur Spine J. 2010;19(1):57-64.[38]Chen IH, Chien JT, Yu TC.Transpedicular wedge osteotomy for correction of thoracolumbar kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis: experience with 78 patients.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(16):E354-360.[39]Wang Y, Zhang Y, Mao K,et al.Transpedicular bivertebrae wedge osteotomy and discectomy in lumbar spine for severe ankylosing spondylitis.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(3): 186-191. [40]Chang KW, Cheng CW, Chen HC,et al. Closing-opening wedge osteotomy for the treatment of sagittal imbalance.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(13):1470-1477. [41]Chen LH, Kao FC, Niu CC,et al.Surgical treatment of spinal pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis.Chang Gung Med J. 2005;28(9):621-628.[42]Tian JW, Wang L, Xia T,et al.Posterior short-segmental fixation combined with intermediate screws vs conventional intersegmental fixation for monosegmental thoracolumbar fractures.Orthopedics. 2011;34(8):e389-396. [43]Aurouer N, Obeid I, Gille O,et al.Computerized preoperative planning for correction of sagittal deformity of the spine.Surg Radiol Anat. 2009;31(10):781-792. [44]Diab MG, Franzone JM, Vitale MG.The role of posterior spinal osteotomies in pediatric spinal deformity surgery: indications and operative technique.J Pediatr Orthop. 2011;31(1 Suppl): S88-98.[45]Smith-Petersen MN, Larson CB, Aufranc OE.Osteotomy of the spine for correction of flexion deformity in rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1969;66:6-9.[46]吕豪珍,林红,张绍昆,等.经伤椎椎弓根置钉技术在胸腰段骨折中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(9):1680-1683.[47]Chang KW, Chen HC, Chen YY,et al.Sagittal translation in opening wedge osteotomy for the correction of thoracolumbar kyphotic deformity in ankylosing spondylitis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(10):1137-1142.[48]Kim KT, Suk KS, Cho YJ,et al.Clinical outcome results of pedicle subtraction osteotomy in ankylosing spondylitis with kyphotic deformity.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(6):612- 618.[49]Hehne HJ, Zielke K, Böhm H.Polysegmental lumbar osteotomies and transpedicled fixation for correction of long-curved kyphotic deformities in ankylosing spondylitis. Report on 177 cases.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;(258): 49-55.[50]van Royen BJ, de Kleuver M, Slot GH.Polysegmental lumbar posterior wedge osteotomies for correction of kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis.Eur Spine J. 1998;7(2):104-10.[51]Willems KF, Slot GH, Anderson PG,et al.Spinal osteotomy in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: complications during first postoperative year.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1): 101-107. [52]朱泽章,邱勇,王斌,等.两种截骨矫形术治疗强直性脊柱炎胸腰椎后凸畸形的围手术期并发症比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2008, 18(12):895-899. [53]Suk SI, Chung ER, Kim JH,et al.Posterior vertebral column resection for severe rigid scoliosis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(14):1682-1687. [54]李书纲,邱贵兴,赵宏,等.后路脊柱截骨治疗强直性脊柱炎后凸畸形[J].中国骨与关节外科,2008,1(2):108-113. [55]Snell BE, Nasr FF, Wolfla CE.Single-stage thoracolumbar vertebrectomy with circumferential reconstruction and arthrodesis: surgical technique and results in 15 patients.Neurosurgery. 2006;58(4 Suppl 2):ONS-263-8; discussion ONS-269. |
| [1] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [2] | Yang Qin, Zhou Honghai, Chen Longhao, Zhong Zhong, Xu Yigao, Huang Zhaozhi. Research status and development trend of pelvic reconstruction techniques: a bibliometric and visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3718-3724. |
| [3] | Zhao Hongshun, A Jiancuo, Wang Deyuan, Xu Zhihua, Gao Shunhong. Factors affecting the height of early intervertebral space after lumbar interbody fusion via lateral approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3332-3336. |
| [4] | Zhang Chongfeng, Li Xianlin, Peng Weibing, Jia Hongsheng, Cai Lei. Treating lumbar disc herniation of blood stasis type with Chinese herbs, acupuncture, moxibustion, and massage: a Bayesian network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2781-2788. |
| [5] |
Zhang Cong, Zhao Yan, Du Xiaoyu, Du Xinrui, Pang Tingjuan, Fu Yining, Zhang Hao, Zhang Buzhou, Li Xiaohe, Wang Lidong.
Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine and pelvis in adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis with lumbar major curve |
| [6] | Tuerhongjiang·Abuduresiti, Meng Xiangyu, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Wang Tiantang, Xieraili·Maimaiti, Dai Jifang, Wang Wei. Biomechanical advantages of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(36): 5768-5773. |
| [7] | Wang Jing, Xu Shuai, Liu Haiying. Hidden blood loss during posterior lumbar interbody fusion in lumbar spinal stenosis patients with and without rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5307-5314. |
| [8] | Shen Canghai, Feng Yongjian, Song Yancheng, Liu Gang, Liu Zhiwei, Wang Ling, Dai Haiyang. Value of quantitative MRI T2WI parameters in predicting surgical outcome of thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2893-2899. |
| [9] |
Wen Yi, Su Feng, Liu Su, Zong Zhiguo, Zhang Xin, Ma Pengpeng, Li Yuexuan, Li Rui, Zhang Zhimin.
Establishment of finite element model of L4-5 and mechanical analysis of degenerative intervertebral discs
|
| [10] | Tian Jie, Ru Jiangying. Preservation of the spinous process ligament complex in expanded decompression of lumbar spinal canal: advantages and disadvantages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1228-1234. |
| [11] | Wang Liang, Li Lijun, Zhu Fuliang, Jiang Zhuyan, Wang Shuai, Ni Dongkui . Cortical bone trajectory screw versus pedicle screw fixation after posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(8): 1291-1298. |
| [12] | Wang Xuefeng, Shang Xifu . Curative effects of three filling materials in the treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 863-869. |
| [13] | Zhou Yu, Liu Yuehong, Liu Shuping, Chen Xi, Qin Wei, Li Qifeng. Spinal stability of intervertebral grafting reinforced by five or six augmenting screws versus transvertebral grafting reinforced by four augmenting screws for thoracolumbar vertebral fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 505-511. |
| [14] | Li Qingsong, Liu Shaoyu, Yin Zongsheng. Multiple posterior lumbar interbody fusion and posterolateral fusion instrumentation for thoracolumbar kyphosis and osteoporotic fracture in older adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 512-517. |
| [15] | Zhu Aiguo, Zhang Feng, Zhu Jianwei, Jin Guohua. Anatomic measurement and clinical significance of the lumbosacral nerve roots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 573-577. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||